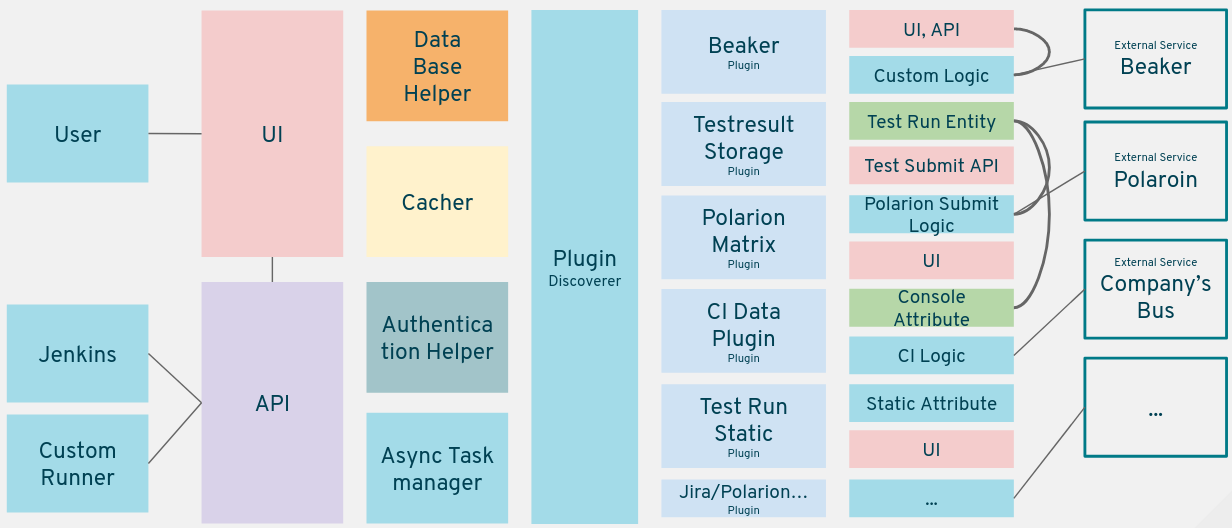
Metadash is powered by Node.js and Flask. Simliar projects could be brought up with tiny adjustment.
Install and Build Dependencies
# Install EPEL for Python 3 and Node.js packages
$ sudo yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
# Dependencies for building python packages
$ sudo yum install -y git python3 python3-devel python3-pip @c-development postgresql-devel
$ sudo pip install pipenv
# Dependencies for building npm packages
$ sudo yum install -y npm bzip2Then build dependencies for both Python and Node.js.
$ [metadash] pipenv install
$ [metadash] pipenv run bin/md-manager setup --devPrepare Database and Redis
We will use container to run both PostgresQL and Redis service.
Install podman and podman-compose. To keep things simple, we will not arrange containers by Kubernetes resources description but instead by podman-compose. Create a docker-compose like YAML file.
version: 3
services:
db:
image: postgres:9.6
restart: always
volumes:
- '/var/lib/metadash-db:/var/lib/postgresql/data'
- './metadash-backups:/var/backups'
ports:
- '5432:5432'
environment:
'POSTGRES_USER': 'metadash'
'POSTGRES_PASSWORD': 'metadash'
cache:
image: redis
volumes:
- '/var/lib/metadash-redis:/data'
ports:
- '6379:6379'
Install podman and podman-compose.
$ sudo yum install -y podman
$ sudo pip install podman-composeThen create data directories and grant SELinux permission to container role.
$ sudo mkdir /var/lib/metadash-db /var/lib/metadash-redis
$ sudo chcon -Rt svirt_sandbox_file_t /var/lib/metadash-db /var/lib/metadash-redisUse podman-compose to create and run the containers.
$ sudo podman-compose -f docker-compose.yml pull
$ sudo podman-compose -f docker-compose.yml up -dConfigure Kerberos Authentication [Optional]
Metadash backend will need to know keytab file and principle for Kerberos authentication. They could be configured via environment variables.
KERBEROS_KEYTAB_FILE=/path/to/key_table_file
KERBEROS_PRINCIPLE=name.principle.example.comIn case of a self-signed or custom certificates, REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE needs to be specified for python-requests library.
REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crtSave the content to metadash.env for later sourcing.
Bring Up Metadash Backend and Frontend
Metadash backend need a database and a message queue to work. By default, it will use postgres://postgres:5432 and redis://redis:6379. Since the database and message queue is running on localhost, we need to add a line to /etc/hosts.
$ sudo echo "127.0.0.1 postgres redis" >> /etc/hostsIf a brand new instance is setup without any test data, a bootstrap to database and an administrator account are needed
$ [metadash] pipenv run bin/md-manager create_database
$ [metadash] pipenv run bin/md-manager create_user --username admin --password passw0rdThen we can bring up Metadash backend and frontend respectively.
$ [metadash] source metadash.env
$ [metadash] pipenv run bin/md-manager runserver -h 127.0.0.1
$ [metadash] npm run ui-devFor running in background and other convenience, running these commands within tmux is recommended.
Nginx Reverse Proxy
Install nginx.
$ sudo yum -y install nginxCreate a simple configuration file at /etc/nginx/conf.d/metadash.conf.
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $server_port;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
}
}
The default UI server is running on port 8080. SELinux policy should be adjusted with a single command without compiling a policy.
$ sudo setsebool httpd_can_network_connect 1 -PStart nginx and you will enjoy a Metadash development server with hot reload.
$ sudo systemctl start nginx
$ sudo systemctl enable nginx
Running Celery Worker [Optional]
Metadash implements a task wrapper mechanism that if no celery worker is online. However, a worker and a beat worker can prevent Metadash from returning timeout error and help with routine jobs.
$ pipenv run celery worker -A metadash.worker.task.celery -l info -n worker@%h
$ pipenv run celery worker -B -A metadash.worker.task.celery -l info -n worker-beat@%h